Where Waters Breathe | Camargue – France | Documentary
- 56 anni
- Documentary
- 240 Views
Can wetlands be restored in landscapes shaped by farming, infrastructure and water control?
In this episode of “Where Waters Breathe”, we travel to the Camargue to explore how climate adaptation depends on managing water, trade-offs and people.
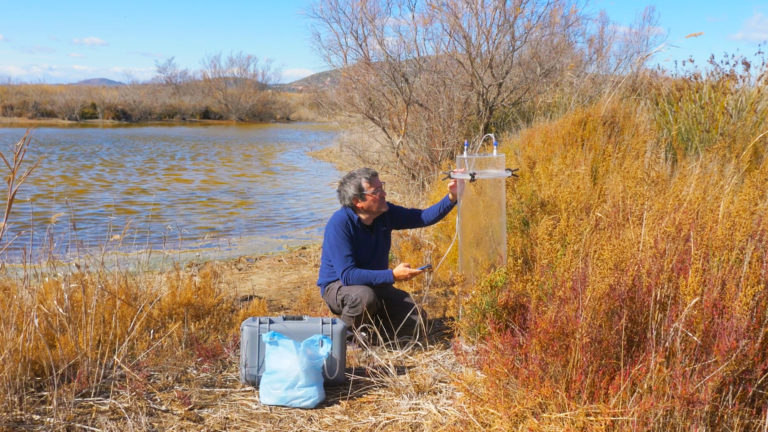
The Camargue, at the heart of the Rhône Delta, is one of Europe’s most complex and intensively managed wetland systems. Spanning nearly 190,000 hectares, it is a vast mosaic of lagoons, brackish marshes, freshwater wetlands, salt steppes, rice paddies and irrigated farmland, all shaped by an engineered hydrological network.
In this episode, scientists, land managers and local actors share their perspectives on wetland restoration in one of Europe’s most complex deltas. The documentary explores how Camargue wetlands provide essential ecosystem services, from flood mitigation and water purification to carbon sequestration, while also supporting agriculture, fishing, cattle grazing, hunting and birdwatching. At the same time, it reveals the fragile trade-offs that shape the region: pesticide use, artificial flooding cycles, invasive species, mosquito outbreaks and increasing pressure on freshwater resources under climate change.
As a RESTORE4Cs Case Pilot, the Camargue functions as a living laboratory for climate-smart wetland management. Researchers study vegetation dynamics, sediment microbial communities and water level fluctuations to better understand carbon cycling and greenhouse gas emissions in managed wetlands. Through restoration and adaptive management strategies, the Camargue offers critical insights into how nature-based solutions can strengthen resilience, recover ecological functions and support climate mitigation in coastal deltas across Europe.
“Where Waters Breathe” is a visually rich documentary series that takes audiences to the living edge of Europe, where land, water, people, and climate meet. Developed within the EU-funded RESTORE4Cs project, this six-episode series journeys across some of Europe’s most emblematic coastal wetlands. From the Valencian Wetlands and the Camargue in the Mediterranean, to the Ria de Aveiro and the South-West Dutch Delta along the Atlantic coast, and onward to the Curonian Lagoon in the Baltic Sea and the Danube Delta in the Black Sea, each episode focuses on one RESTORE4Cs Case Pilot. Together, they showcase wetlands in different states of preservation, from well-conserved to heavily altered, and the diverse restoration solutions being tested and implemented across Europe.
Follow RESTORE4Cs’ Where Waters Breathe:
Website: https://www.restore4cs.eu/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/restore4c
BlueSky: https://bsky.app/profile/restore4cs.bsky.social
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/restore4cs/
Where Waters Breathe | Ria de Aveiro – Portugal | Documentary
- 56 anni
- Documentary
- 162 Views
In the Ria de Aveiro, tides, salt and freshwater shape both nature and identity.
This episode of “Where Waters Breathe” explores how one of Portugal’s most emblematic lagoons is adapting to climate change, erosion and shifting livelihoods.
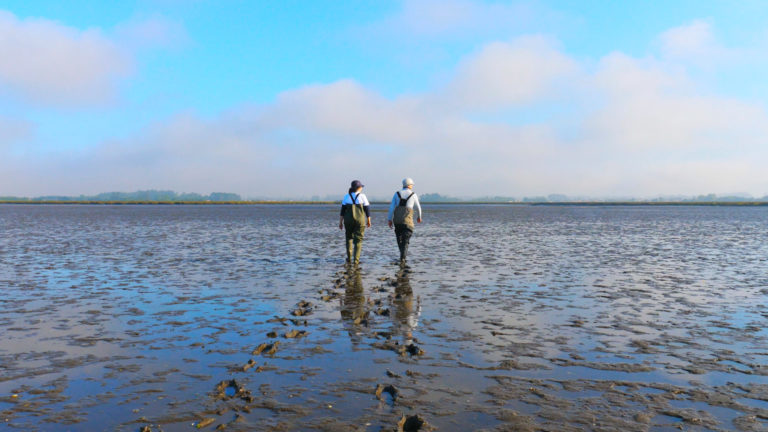
The Ria de Aveiro, in central Portugal, is a shallow coastal lagoon where freshwater from the Vouga River meets Atlantic tides through a single ocean inlet. Covering around 11,000 hectares, it forms a complex mosaic of salt marshes, mudflats, seagrass meadows, dunes, bocage farmland and freshwater lagoons, one of Europe’s most diverse coastal wetland systems.
Classified under the Natura 2000 network and including Ramsar and Natural Reserve sites, the Ria de Aveiro is both a biodiversity hotspot and a socio-ecological landscape supporting 356,000 residents across ten municipalities. Traditional activities – fishing, shellfish gathering, salt production and agriculture – coexist with industrial development, tourism and growing recreational use.
In this episode, fishermen, salt workers, forest managers, sports coaches, environmental educators and scientists share how the lagoon has changed over decades. While pollution has declined, other pressures have intensified: stronger tidal dynamics, increased saltwater intrusion, erosion of banks and disappearance of salt pans and seagrass habitats. Channels deepen and widen, islands shrink, and historic habitats for species such as the European eel have declined.
Climate change intensifies these challenges. Prolonged droughts, rising sea levels and altered hydrology reshape both the lagoon and the surrounding forests. Increased tidal prism and water velocities raise turbidity and fragment habitats, threatening marshes and Zostera seagrass beds that once stabilised sediments and sheltered marine life.
At the heart of the lagoon operates a long-term socio-ecological research platform (LTsER), turning the Ria into a real-time observatory. Within the RESTORE4Cs Case Pilot, researchers restore priority seagrass habitats and seasonally measure carbon storage and greenhouse gas exchanges – CO₂, CH₄ and N₂O – across preserved, altered and restored sites. These data feed GIS-based models that simulate future climate scenarios and evaluate how restoration can enhance blue carbon capacity, sediment stability and ecosystem resilience.
Beyond science, the episode highlights the importance of integrated governance and local engagement. Restoration efforts rely not only on monitoring and modelling, but also on citizen science, stakeholder dialogue and collaboration between universities, NGOs, municipalities and lagoon users. In the Ria de Aveiro, ecological recovery depends on reconnecting people with the lagoon – culturally, economically and emotionally.
“Where Waters Breathe” is a visually rich documentary series that takes audiences to the living edge of Europe, where land, water, people, and climate meet. Developed within the EU-funded RESTORE4Cs project, this six-episode series journeys across some of Europe’s most emblematic coastal wetlands. From the Valencian Wetlands and the Camargue in the Mediterranean, to the Ria de Aveiro and the South-West Dutch Delta along the Atlantic coast, and onward to the Curonian Lagoon in the Baltic Sea and the Danube Delta in the Black Sea, each episode focuses on one RESTORE4Cs Case Pilot. Together, they showcase wetlands in different states of preservation, from well-conserved to heavily altered, and the diverse restoration solutions being tested and implemented across Europe.
Follow RESTORE4Cs’ Where Waters Breathe:
Website: https://www.restore4cs.eu/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/restore4c
BlueSky: https://bsky.app/profile/restore4cs.bsky.social
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/restore4cs/
Where Waters Breathe | South-West Dutch Delta – Netherlands| Documentary
- 56 anni
- Documentary
- 137 Views
How do salt marshes protect the Netherlands from floods, and what happens when natural systems are altered?
In this episode of “Where Waters Breathe”, we explore the South-West Dutch Delta, where engineering, ecology and climate adaptation collide.
The South-West Dutch Delta, where the Rhine, Maas and Scheldt rivers meet the North Sea, is a dynamic landscape of mudflats, sand dunes, tidal marshes and wetlands. After the devastating 1953 flood, the area was reshaped by the Delta Works – a monumental system of dams, locks and storm surge barriers that dramatically improved water safety, while also altering natural tidal dynamics.
Today, this transformed delta faces new challenges. Erosion, declining sedimentation, water quality issues and “sand starvation” affect coastal channels and salt marshes, while industrial activity, shipping, agriculture and climate change put increasing pressure on these fragile ecosystems.
In this episode, scientists and practitioners reflect on the critical role of wetlands in supporting biodiversity, providing nursery habitats for fish, hosting migratory birds, storing carbon, and reducing wave energy. As a RESTORE4Cs Case Pilot, the South-West Dutch Delta is also a testing ground for climate-adapted wetland restoration, exploring how nature-based solutions can strengthen flood protection, improve water quality and support long-term climate resilience.
The episode highlights ongoing research, including blue carbon assessments and integrated water management strategies, while emphasising the importance of long-term planning, interdisciplinary science and local community involvement. As sea levels rise and existing infrastructures age, the future of the Delta depends on decisions being made today, at the interface between water, land, nature and society.
“Where Waters Breathe” is a visually rich documentary series that takes audiences to the living edge of Europe, where land, water, people, and climate meet. Developed within the EU-funded RESTORE4Cs project, this six-episode series journeys across some of Europe’s most emblematic coastal wetlands. From the Valencian Wetlands and the Camargue in the Mediterranean, to the Ria de Aveiro and the South-West Dutch Delta along the Atlantic coast, and onward to the Curonian Lagoon in the Baltic Sea and the Danube Delta in the Black Sea, each episode focuses on one RESTORE4Cs Case Pilot. Together, they showcase wetlands in different states of preservation, from well-conserved to heavily altered, and the diverse restoration solutions being tested and implemented across Europe.
Follow RESTORE4Cs’ Where Waters Breathe:
Website: https://www.restore4cs.eu/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/restore4c
BlueSky: https://bsky.app/profile/restore4cs.bsky.social
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/restore4cs/
Where Waters Breathe | Danube Delta – Romania | Documentary
- 56 anni
- Documentary
- 139 Views
What happens when water disappears from one of Europe’s wildest deltas?
In this episode of “Where Waters Breathe”, we journey into the Danube Delta, a shifting mosaic of water, reeds and communities where restoration, tradition and climate resilience meet.
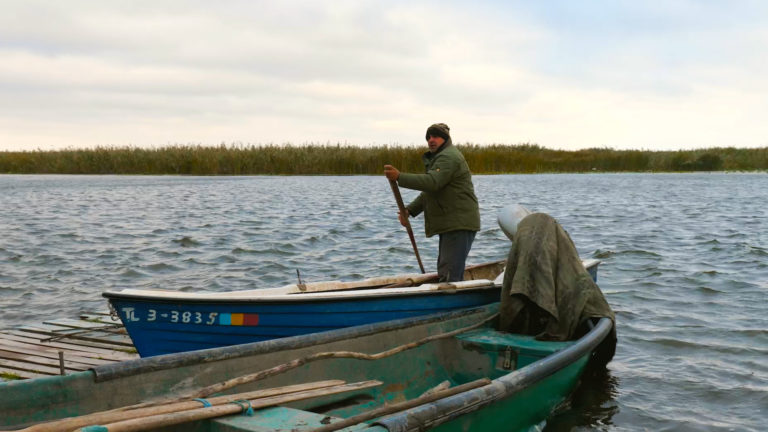
The Danube Delta is Europe’s second-largest delta and one of the world’s best-preserved wetland systems. Stretching across 5,800 km² of channels, lakes, reed beds and marshes, it hosts more than 5,000 species and forms one of the continent’s richest biodiversity hotspots.
In this episode, fishermen, scientists, foresters and local entrepreneurs share their perspectives on how the Delta has changed over recent decades. From communist-era land reclamation and agricultural systematisation to more recent restoration initiatives, the landscape has continuously shifted between natural dynamics and human intervention.
The film explores how past agricultural systematisation altered large wetland areas, transforming parts of the Delta into arid farmland. Today, ecological reconstruction projects aim to restore water circulation, reopen canals and improve habitat quality, benefiting fish reproduction, bird nesting areas and local livelihoods.
As a sanctuary along the East Atlantic Flyway, the Delta hosts hundreds of migratory bird species, including Dalmatian pelicans and white-tailed eagles. Fishing, reed harvesting and eco-tourism remain deeply intertwined with this wetland system, demonstrating how culture and biodiversity are inseparable in the Delta’s identity.
Despite its resilience, the Danube Delta faces growing pressures from pollution, invasive species, plastic contamination and climate-driven warming. As a UNESCO World Heritage Site and Ramsar wetland, the Danube Delta is also a key research site within RESTORE4Cs. Researchers conducted seasonal field campaigns measuring carbon storage and greenhouse gas fluxes – CO₂, CH₄ and N₂O – across preserved, altered and restored wetlands. These data feed predictive models assessing how restoration can strengthen the Delta’s function as a carbon sink while enhancing climate resilience.
Ultimately, the episode highlights a simple but powerful message echoed by local communities: water is the foundation of everything. Without healthy water circulation, biodiversity declines, fisheries suffer and tourism falters. In the Danube Delta, restoration is not only about conservation: it is about securing a future where nature, culture and climate adaptation move forward together.
“Where Waters Breathe” is a visually rich documentary series that takes audiences to the living edge of Europe, where land, water, people, and climate meet. Developed within the EU-funded RESTORE4Cs project, this six-episode series journeys across some of Europe’s most emblematic coastal wetlands. From the Valencian Wetlands and the Camargue in the Mediterranean, to the Ria de Aveiro and the South-West Dutch Delta along the Atlantic coast, and onward to the Curonian Lagoon in the Baltic Sea and the Danube Delta in the Black Sea, each episode focuses on one RESTORE4Cs Case Pilot. Together, they showcase wetlands in different states of preservation, from well-conserved to heavily altered, and the diverse restoration solutions being tested and implemented across Europe.
Follow RESTORE4Cs’ Where Waters Breathe:
Website: https://www.restore4cs.eu/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/restore4c
BlueSky: https://bsky.app/profile/restore4cs.bsky.social
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/restore4cs/
Where Waters Breathe | Curonian Lagoon – Lithuania | Documentary
- 56 anni
- Documentary
- 127 Views
What happens when too many nutrients enter a shallow coastal lagoon?
In this episode of “Where Waters Breathe”, we explore the Curonian Lagoon, Europe’s largest coastal lagoon, where eutrophication, climate change and cross-border governance collide.
The Curonian Lagoon, stretching across Lithuania and Russia, is one of the most eutrophication-sensitive ecosystems in the Baltic region. Shallow, wide and highly dynamic, the lagoon receives massive inflows of freshwater, sediment and nutrients from the Nemunas River, creating conditions that fuel intense late-summer cyanobacteria blooms.
In this episode, researchers reflect on how decades of human pressure have reshaped the lagoon. During the Soviet period, uncontrolled agricultural and industrial inputs severely degraded water quality. Since Lithuania joined the European Union, new water quality measures have been implemented, leading to visible improvements in some restored areas – including clearer water, deeper aquatic vegetation and renewed recreational use. Yet monitoring data and satellite observations show that much of the lagoon still fails to reach good ecological status.
The documentary follows scientists working to understand nutrient cycling and eutrophication processes in the lagoon. Rather than relying only on costly trial-and-error interventions, the team uses ecological models to simulate restoration scenarios and predict which measures could most effectively reduce nutrient loads, limit harmful algal blooms and lower greenhouse gas emissions. These tools help identify solutions that can be applied not only locally, but across similar coastal systems in Europe.
The film also highlights the lagoon’s broader ecological and social context. At its southern edge, the Nemunas Delta – a RAMSAR-protected wetland on the East Atlantic Flyway – supports rich biodiversity and long-standing human activities, from farming and fishing to ecotourism. Along the western shore, the Curonian Spit’s iconic dunes and forests draw hundreds of thousands of visitors each year, even as warming waters, invasive species and shifting salinity signal rapid environmental change.
A key challenge emerges clearly: the Curonian Lagoon is a shared ecosystem. With only part of the lagoon under Lithuanian jurisdiction, effective restoration depends on cross-border cooperation and coordinated management. The episode underscores how scientific knowledge, modelling and dialogue between neighbouring countries are essential to restoring water quality and building long-term resilience in one of Europe’s most emblematic coastal wetlands.
“Where Waters Breathe” is a visually rich documentary series that takes audiences to the living edge of Europe, where land, water, people, and climate meet. Developed within the EU-funded RESTORE4Cs project, this six-episode series journeys across some of Europe’s most emblematic coastal wetlands. From the Valencian Wetlands and the Camargue in the Mediterranean, to the Ria de Aveiro and the South-West Dutch Delta along the Atlantic coast, and onward to the Curonian Lagoon in the Baltic Sea and the Danube Delta in the Black Sea, each episode focuses on one RESTORE4Cs Case Pilot. Together, they showcase wetlands in different states of preservation, from well-conserved to heavily altered, and the diverse restoration solutions being tested and implemented across Europe.
Follow RESTORE4Cs’ Where Waters Breathe:
Website: https://www.restore4cs.eu/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/restore4c
BlueSky: https://bsky.app/profile/restore4cs.bsky.social
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/restore4cs/
Where Waters Breathe | Valencian Wetlands – Spain | Documentary
- 56 anni
- Documentary
- 155 Views
Along the Valencian coast, small wetlands carry a long history and a fragile future.
In this episode of “Where Waters Breathe”, we explore the Marjal dels Moros, a coastal marsh where restoration, community action and climate resilience converge.
The Marjal dels Moros, a 620-hectare coastal wetland near Valencia, is one of the last surviving fragments of the extensive marshes that once stretched uninterrupted along the Mediterranean coast between the Ebro Delta and the Segura River. Today, surrounded by urban expansion, agriculture and industrial estates, it remains a rare and biodiverse enclave shaped by brackish waters, sediment flows from the Palancia River and centuries of human interaction.
Despite its modest size, the marsh supports remarkable biodiversity. Endangered fish such as Aphanius iberus and Valencia hispanica, rare crustaceans like Palaemonetes zariquieyi, and a rich community of migratory birds find refuge in its reedbeds, open waters and brackish channels. The site forms part of Natura 2000 and includes Special Protection Areas and Microreserves safeguarding priority habitats.
In this episode, environmental educators, fishers, conservationists and researchers recount decades of efforts to protect and restore this wetland. Once rice fields and agricultural mosaics, parts of the area were abandoned after industrial restructuring in the late 20th century. Following forty years of advocacy by local environmental groups, legal protection was secured, allowing restoration projects to begin in the 1990s.
Restoration actions have re-established water circulation, reopened channels, replanted macrophytes and reintroduced grazing as a tool for vegetation management. Maintaining good-quality water, and ensuring the proper functioning of sluice gates that connect marsh and sea, has been essential for ecological recovery. The return of young eels and the gradual improvement of habitat conditions testify to these efforts.
Yet the marsh remains under pressure. Urban development, industrial expansion, aquifer overuse and altered hydrology threaten water inputs and connectivity. New infrastructure risks increasing runoff pollution and disrupting fragile sediment balances. Local actors emphasise that wetlands not only host biodiversity, but also protect coastal towns from flooding and help regulate water quality and climate impacts.
As part of the RESTORE4Cs Case Pilot, researchers from the University of Valencia monitor soil, vegetation and hydrological recovery, measuring greenhouse gas fluxes – CO₂ and methane – to evaluate the marsh’s role in climate mitigation. Healthy wetlands act as carbon sinks; degraded ones can become sources of emissions. Through modelling and field experiments, the project assesses how brackish marsh restoration can enhance blue carbon storage while strengthening resilience to sea-level rise.
The episode ultimately reveals that the future of Valencian wetlands depends on alliances between public administration, local communities, NGOs, researchers and even private companies. In the Marjal dels Moros, restoration is not only about protecting a habitat, but about redefining how Mediterranean coastal landscapes can adapt to climate change while sustaining both biodiversity and society.
“Where Waters Breathe” is a visually rich documentary series that takes audiences to the living edge of Europe, where land, water, people, and climate meet. Developed within the EU-funded RESTORE4Cs project, this six-episode series journeys across some of Europe’s most emblematic coastal wetlands. From the Valencian Wetlands and the Camargue in the Mediterranean, to the Ria de Aveiro and the South-West Dutch Delta along the Atlantic coast, and onward to the Curonian Lagoon in the Baltic Sea and the Danube Delta in the Black Sea, each episode focuses on one RESTORE4Cs Case Pilot. Together, they showcase wetlands in different states of preservation, from well-conserved to heavily altered, and the diverse restoration solutions being tested and implemented across Europe.
Follow RESTORE4Cs’ Where Waters Breathe:
Website: https://www.restore4cs.eu/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/restore4c
BlueSky: https://bsky.app/profile/restore4cs.bsky.social
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/restore4cs/
Top 3 video contents of the month
Women in Science
Browse by topic
Biodiversity & ecosystems
Climate change & human pressures
- 29 November 2023
- Teaser
- 29 November 2023
- Interviews
- 11 November 2022
- Interviews
- 12 October 2022
- Field research
- 25 May 2022
- Alien species
Conservation & restoration
Sustainable development
- 29 November 2023
- Interviews
- 29 November 2023
- Interviews
- 29 November 2023
- Interviews
- 29 November 2023
- Interviews
- 29 November 2023
- Interviews
- 29 November 2023
- Interviews
- 20 June 2023
- Interviews
- 17 February 2023
- Interviews
LifeWatch ERIC advancements
Education
- 05 March 2024
Awards
What's new on the LifeWatch ERIC National TV channels
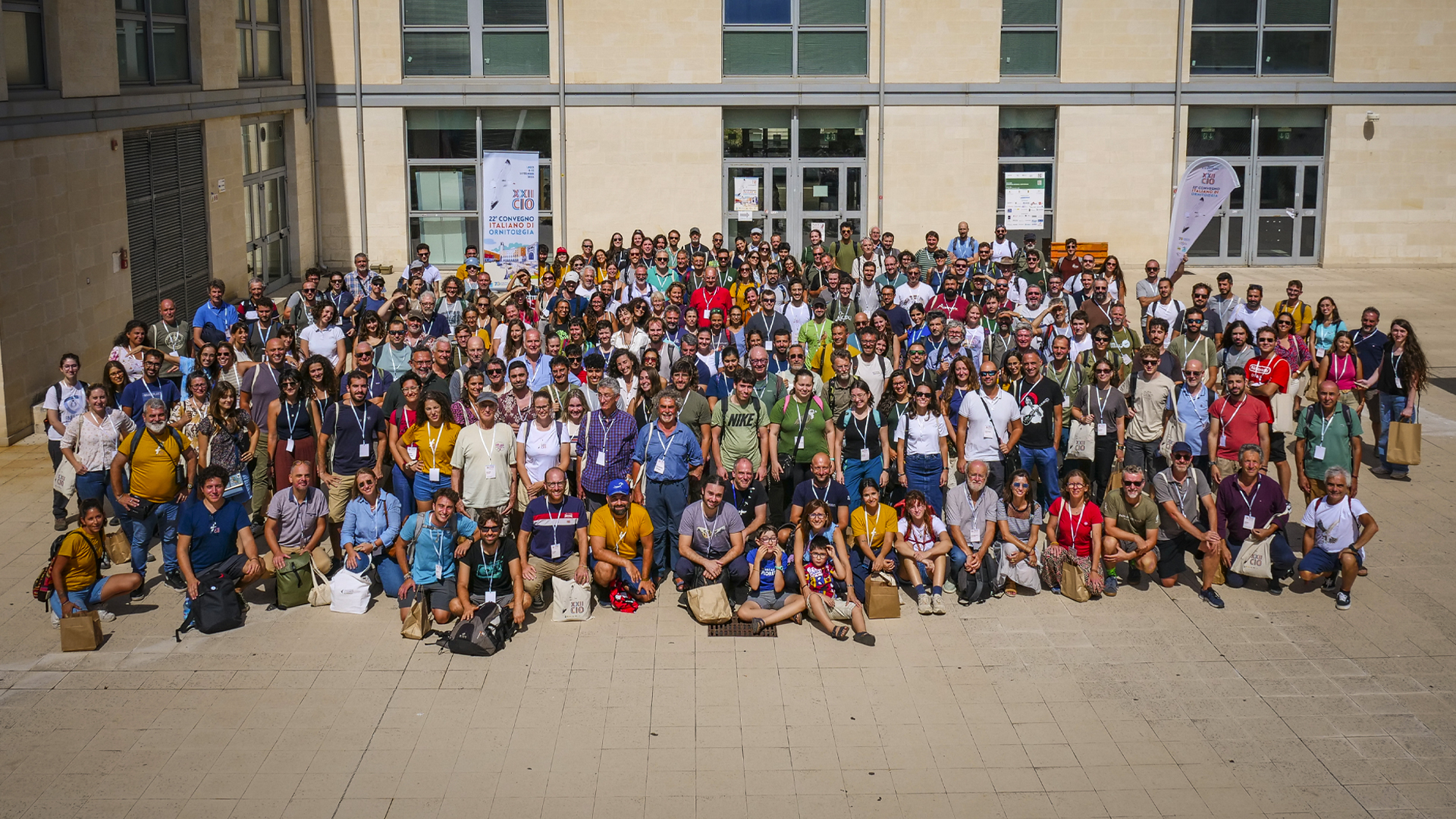
22° CIO – Convegno Italiano di Ornitologia – Lecce 2025
22° CIO – Convegno Italiano di Ornitologia
Per la prima volta in Puglia è stato ospitato il Convegno Italiano di Ornitologia, giunto alla sua ventiduesima edizione. L’incontro, in programma dall’8 al 12 settembre a Lecce, è organizzato congiuntamente da CISO (Centro Italiano Studi Ornitologici), CNR-IRET (Istituto di Ricerca sugli Ecosistemi Terrestri del Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche), Università del Salento, LifeWatch Italy, Or.Me. e NBFC con l’obiettivo di riunire ricercatori, tecnici, enti gestori e associazioni impegnate nello studio e nella conservazione dell’avifauna. Per l’occasione, l’evento è stato arricchito da una mostra fotografica dal titolo “Cambiamo Rotta! Immagini per un percorso di conservazione più efficace”, frutto della collaborazione tra AFNI (Associazione Fotografi Naturalisti Italiani), Lipu (Lega Italiana Protezione Uccelli) e CISO.
Alla scoperta della biodiversità nascosta – Progetto ITINERIS Scuole 2025
ALLA SCOPERTA DELLA BIODIVERSITA’ NASCOSTA – Progetto ITINERIS Scuole 2025
Gli studenti degli Istituti Comprensivi di Salve, Supersano e Alliste, insieme agli Ambiti Sociali di Casarano e Poggiardo, hanno vissuto un’esperienza ad alto valore scientifico presso il CNR-IRET e il DISTEBA di UniSalento. ITINERIS, insieme con l’Università di Bari e LifeWatch, hanno organizzato questa esperienza per rendere le infrastrutture di ricerca più vicine ai ragazzi ed alla società alla scoperta della biodiversità nascosta. Attraverso la collaborazione con scuole, comuni e organizzazioni del Terzo Settore, si lavora per misurare e potenziare l’impatto sociale delle infrastrutture di ricerca, combattere la povertà educativa, valorizzare gli ecosistemi ambientali locali, rafforzare la partecipazione attiva nei territori.
Un passo concreto per una Ricerca più inclusiva e orientata al bene comune.
#ITINERIS #UniSalento #CPM UniSalento #DiSTeBA UniSalento #LifeWatch #CNR #UniversitàDiBari #PovertàEducativa #InnovazioneSociale #ImpattoSociale
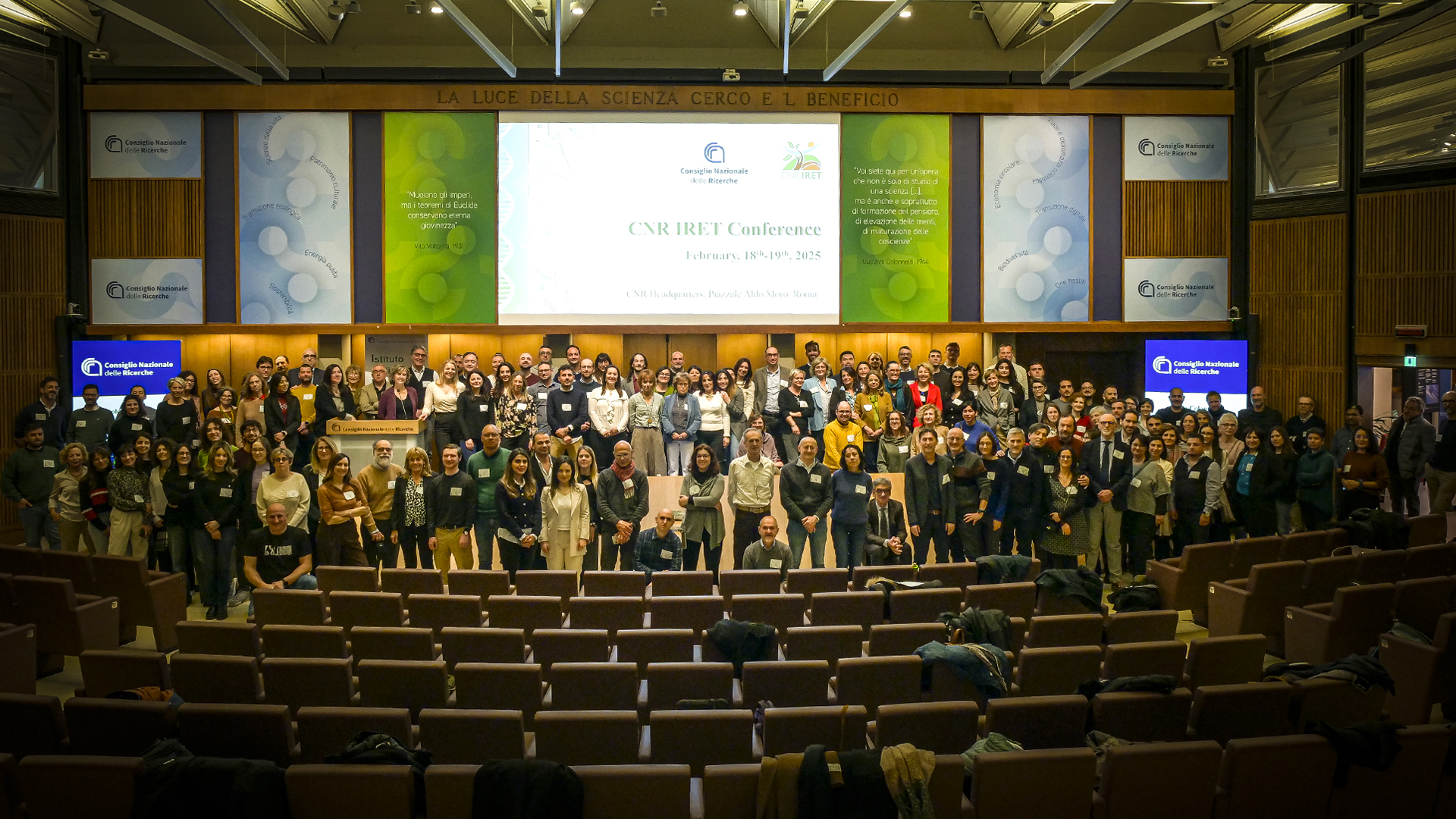
Conferenza CNR-IRET: prospettive per una gestione integrata degli ecosistemi
Nature-Based Solutions per la riqualificazione degli ambienti degradati; indicatori di biodiversità, capaci di darci un’idea della qualità degli habitat, e di dove e come intervenire per migliorare il loro stato di salute; l’effetto degli inquinanti sugli ecosistemi; le risposte degli ecosistemi agli incendi; le sfide dell’IA applicata alla conservazione della biodiversità e degli ecosistemi; il legame tra ambiente e salute; gli impatti legati ai cambiamenti climatici; l’importanza della ricerca e delle collaborazioni internazionali: sono solo alcuni dei temi del ricco programma della Conferenza CNR IRET “Risultati e prospettive per la gestione integrata degli ecosistemi del futuro”, a Roma il 18-19 febbraio 2025 presso la sede centrale del Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR).
Come ha affermato ai nostri microfoni il suo Direttore, Carlo Calfapietra, con quasi 250 dipendenti e 7 sedi in tutta Italia, l’Istituto di Ricerca sugli Ecosistemi Terrestri (IRET) è un istituto in crescita, in grado portare avanti una ricerca all’avanguardia e di dare importanti contributi nella definizione della Nature Restoration Law e delle altre politiche di conservazione degli ecosistemi.
Guarda il video! Con interventi di:
- Carlo Calfapietra – Direttore CNR IRET
- Paolo Colangelo – Primo Tecnologo CNR IRET
- Jingjing Liang – Professore associato, University of Purdue
- Grazia Masciandaro – Dirigente di ricerca, CNR IRET
- Paola Bonfante – Professoressa emerita, Università di Torino
- Elena Paoletti – Dirigente di ricerca, CNR IRET
- Diego Fontaneto – Dirigente di ricerca, IRSA CNR
- Alberto Battistelli – Dirigente di ricerca, CNR IRET
Video realizzato da Fabrizio Lecce CPM – Centro Produzione Multimediale UniSalento LifeWatching WebTv in occasione della conferenza d’Istituto del CNR IRET.
EcologicaCup 2024: la cerimonia di premiazione delle scuole vincitrici
Il 21 maggio 2024, nel corso della Settimana della Biodiversità Pugliese, si è svolta la cerimonia di premiazione di EcoLogicaCup 2024, la competizione nazionale di Ecologia e Sostenibilità per le scuole primarie e secondarie. L’edizione di quest’anno s’inseriva tra le iniziative del Festival dello Sviluppo Sostenibile ed era patrocinata dalla RUS – Rete delle Università per lo Sviluppo Sostenibile.
Coordinato dal Prof. Alberto Basset e dalla dott.ssa Franca Sangiorgio, il progetto EcoLogicaCup è promosso e organizzato dal Laboratorio di Ecologia e dal Museo su Ecologia degli Ecosistemi Mediterranei del Dipartimento di Scienze e Tecnologie Biologiche e Ambientali UniSalento, in collaborazione con LifeWatch Italia.
EcoLogicaCup, la gara nazionale di ecologia per le scuole | Spot
EcoLogicaCup è una gara nazionale a squadre, completamente online, per approfondire tematiche di ecologia, educazione ambientale e sostenibilità con gli studenti della scuola primaria e secondaria. La partecipazione alla competizione prevede la registrazione gratuita delle squadre su una piattaforma, approfondimenti di ecologia consultabili e scaricabili, sessioni di allenamento e gara finale. Sotto la guida di un docente tutor, le squadre partecipano alla gara finale, dopo aver superato le selezioni attraverso una serie di allenamenti online con quiz a risposta multipla sulle tematiche di gara. Le migliori squadre degli allenamenti e i vincitori assoluti della competizione finale ricevono dei premi nel corso di una cerimonia ufficiale.
EcoLogicaCup riconosce nei giovani la componente sociale maggiormente ricettiva ai valori ambientali, pronta a modificare i propri comportamenti e a promuovere un cambiamento dei comportamenti anche delle altre fasce generazionali. EcoLogicaCup vuole contribuire allo sviluppo di una cultura sempre più orientata verso la sostenibilità, con l’auspicio di formare futuri cittadini più consapevoli rispetto alle tematiche ambientali.
Le attività si collocano nel panorama definito dall’Agenda 2030 per lo Sviluppo Sostenibile, in particolare in riferimento agli Obiettivi 13, 14 e 15. Incentrata sull’uso del web, EcoLogicaCup promuove un’Educazione 3.0 dove gli studenti sono creatori di artefatti di conoscenza che condividono tra loro, rendendo il processo d’insegnamento-apprendimento un’esperienza più stimolante.
Per iscriversi e partecipare visita la piattaforma dedicata a EcologicaCup
Contatti: Dott.ssa Franca Sangiorgio
ecologicacup@unisalento.it
+39 0832 298606
Transizioni ecologiche: i Cammini di LTER Italia
Dal Mar Piccolo ad Acquatina, il cammino in bicicletta di LTER Italia collega, in tre giorni, due importanti siti della ricerca ecologica di lungo termine. La natura degli ambienti di transizione del Mar Piccolo di Taranto e di Acquatina di Leccce ispira un percorso che si snoda attraverso un territorio che passa dal mare alla terra.
L’iniziativa rientra tra gli obiettivi del National Biodiversity Future Center (NBFC) di conservare, ripristinare, monitorare e valorizzare la biodiversità italiana e mediterranea. Per maggiori informazioni, visita il sito ufficiale LTER-IT
“La foresta invisibile” finalista al concorso Rai “Prix Italia 2023”
“La foresta invisibile” è il documentario realizzato dagli studenti del laboratorio di film-making del corso di laurea in Discipline delle Arti, della Musica e dello Spettacolo (DAMS) dell’Università del Salento, condotto dal Prof. Luca Bandirali e coordinato dal dott. Emiliano Carico e dal dott. Fabrizio Lecce. Il progetto, realizzato in collaborazione con LifeWatch ERIC, il consorzio per un’infrastruttura europea di e-Science e Tecnologia per la ricerca su biodiversità ed ecosistemi, è stato presentato al Prix Italia 2023 Concorso internazionale per Radio, TV e Web della Rai.
Protagonista del video è il Phytoplankton, elemento invisibile a occhio nudo, fonte essenziale di energia per gli ecosistemi marini e non solo.
Il progetto è frutto di una collaborazione tra dipartimenti (Beni Culturali, DAMS e DiSTeBA), e nasce con l’obiettivo di sensibilizzare l’opinione pubblica sul tema della ricerca scientifica e delle energie rinnovabili.
EcologicaCup 2023: la premiazione al Festival dello Sviluppo Sostenibile
Cerimonia di premiazione di EcoLogicaCup 2023, Competizione nazionale di Ecologia e Sostenibilità per le scuole primarie e secondarie.
EcoLogicaCup è promossa e organizzata dal Laboratorio di Ecologia e dal Museo su Ecologia degli Ecosistemi Mediterranei del Dipartimento di Scienze e Tecnologie Biologiche e Ambientali, in collaborazione con LifeWatch Italia.
L’edizione di quest’anno è tra le iniziative del Festival dello Sviluppo Sostenibile ed è patrocinata dalla RUS – Rete delle Università per lo Sviluppo Sostenibile. Progetto coordinato da Alberto Basset e Franca Sangiorgio.

22° CIO – Convegno Italiano di Ornitologia – Lecce 2025

Alla scoperta della biodiversità nascosta – Progetto ITINERIS Scuole 2025

Conferenza CNR-IRET: prospettive per una gestione integrata degli ecosistemi

EcologicaCup 2024: la cerimonia di premiazione delle scuole vincitrici

EcoLogicaCup, la gara nazionale di ecologia per le scuole | Spot

Transizioni ecologiche: i Cammini di LTER Italia

“La foresta invisibile” finalista al concorso Rai “Prix Italia 2023”